Steel Angle Iron: Definition, Features, and Uses
Steel angle iron, also known as steel angle or angle bar, is one of the most widely used structural steel products in construction and manufacturing. Thanks to its simple shape, high strength, and cost efficiency, it plays a key role in many load-bearing and support applications. This article explains what steel angle iron is, how it is made, its main types, key features, and common uses.
What Is Steel Angle Iron?
Steel angle iron is a long steel product with an L-shaped cross section. It consists of two legs that meet at a 90-degree angle. These legs can be equal in length or unequal, depending on design requirements.
Most angle irons are made from carbon steel, which offers a good balance of strength, toughness, and affordability. Due to its structural stability, steel angle iron is commonly used to support loads, reinforce frames, and connect components in various engineering projects.
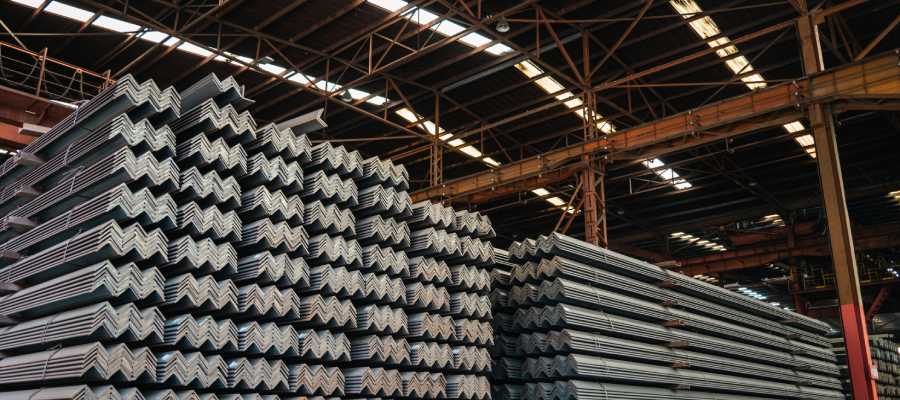

Steel Angle Iron Manufacturing Process
Steel angle iron is typically produced through the hot rolled process. In this method, steel billets are heated to a high temperature above the recrystallization point and then rolled into the required angle shape.
Hot rolling provides several advantages:
Good mechanical strength
Uniform internal structure
Cost-effective production for large volumes
After rolling, the angles are cooled naturally, cut to length, and may undergo further surface treatment such as galvanizing or painting for corrosion protection.
Types of Steel Angle Iron
Steel angle iron can be classified in several ways based on leg size, surface treatment, and standards.
1. Equal Angle Steel
Both legs have the same width. This type is widely used in structural frameworks, towers, and general fabrication due to its balanced strength.
2. Unequal Angle Steel
The two legs have different widths. This design is suitable for applications where load distribution or space constraints require asymmetric support.
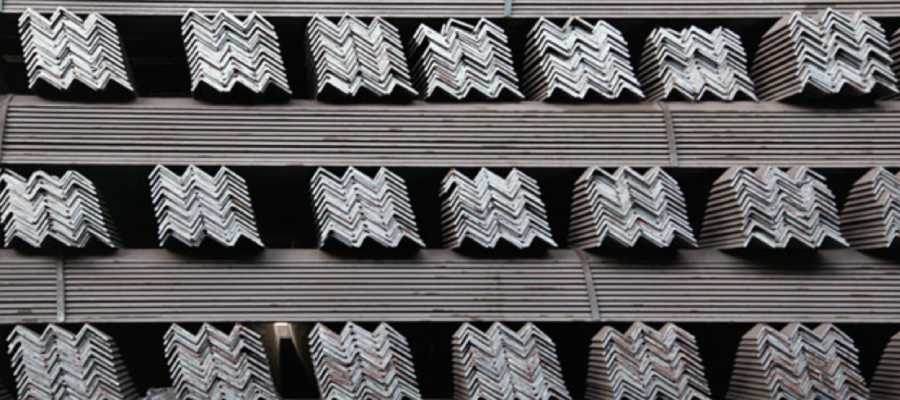

3. Galvanized Steel Angle
This type is coated with zinc to improve corrosion resistance. It is ideal for outdoor structures, humid environments, and coastal areas.
4.Hot Rolled Steel Angle
Manufactured by hot rolling process.
Offers good toughness and is suitable for heavy-duty applications.

Key Features and Advantages
Steel angle iron offers several important benefits that make it a preferred structural material:
High Strength and Load Capacity
The L-shape provides excellent resistance to bending and torsion, making it suitable for heavy loads.
Versatility
It can be cut, welded, drilled, and bolted easily, allowing flexible use in different projects.
Cost Efficiency
Compared with more complex steel sections, angle iron is economical while still providing reliable performance.
Wide Size Range
Available in various thicknesses and leg dimensions to meet different engineering needs.
Durability
When made from carbon steel and properly protected, it offers a long service life.
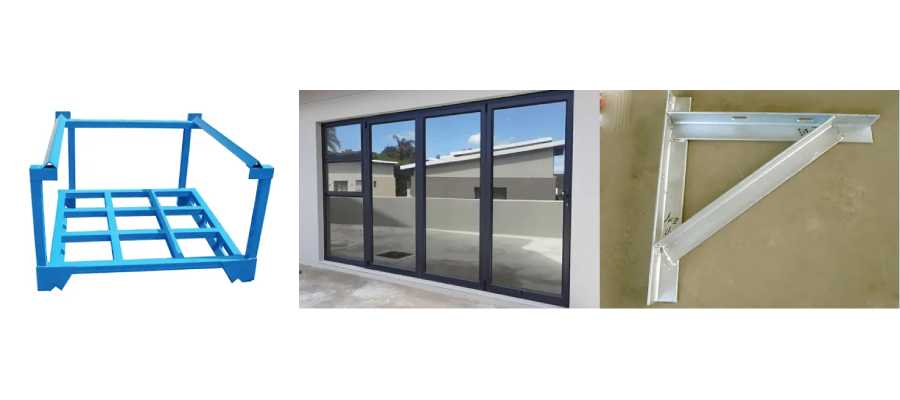
Common Applications of Steel Angle Iron
Because of its structural stability and adaptability, steel angle iron is used across many industries.
Construction and Infrastructure
In building projects, steel angle iron is used for:
Structural frames
Bracing and reinforcement
Stair supports
Roof trusses
It helps improve overall stability and load distribution in steel structures.
Manufacturing and Fabrication
Angle iron is widely applied in:
Machine frames
Equipment supports
Storage racks
Work platforms
Its ease of fabrication makes it ideal for custom metalwork.
Power and Communication Structures
Steel angle iron is commonly used in:
Transmission towers
Communication masts
Substation structures
Its strength and dimensional stability are critical for tall and exposed structures.

Transportation and Industrial Projects
It is also used in:
Railway components
Truck and trailer frames
Industrial shelving systems
In these applications, reliability and structural integrity are essential.

Standards and Specifications
Steel angle iron is produced according to international and regional standards to ensure quality and performance. Common standards include:
ASTM (such as ASTM A36)
EN standards
JIS standards
GB standards
Different grades define chemical composition, mechanical properties, and tolerances, allowing buyers to select the right product for their project.
Choosing the Right Steel Angle Iron
When selecting steel angle iron, consider the following factors:
Load requirements
Environmental conditions
Required size and thickness
Surface treatment needs
Applicable standards
For outdoor or corrosive environments, galvanized or coated angle iron is recommended.
Conclusion
Steel angle iron is a fundamental structural material known for its strength, versatility, and affordability. Made mainly from carbon steel through the hot rolled process, it is available in multiple types and sizes to suit a wide range of applications. From construction and infrastructure to manufacturing and industrial projects, steel angle iron continues to be a reliable solution for structural support and reinforcement.
Understanding its features and proper uses can help engineers, contractors, and buyers choose the right angle iron for long-lasting and cost-effective performance.











